What are some ways that cells can help organisms?
1. Μεταβολισμός:
* Παραγωγή ενέργειας: Cells generate energy through processes like cellular respiration, breaking down nutrients to power cellular activities.
* Επεξεργασία θρεπτικών ουσιών: Cells take in nutrients, break them down, and synthesize new molecules needed for growth and repair.
* Αφαίρεση αποβλήτων: Cells eliminate waste products of metabolism.
2. Ανάπτυξη και ανάπτυξη:
* Κυτταρική διαίρεση: Cells divide to create new cells, enabling growth, repair, and reproduction.
* Διαφοροποίηση: Cells specialize to perform specific functions, contributing to the development of tissues and organs.
* Μορφογένεση: Cells coordinate their movement and interactions to shape tissues and organs.
3. Δομή και υποστήριξη:
* δομικά στοιχεία: Cells form tissues and organs, providing structural support and shape to the organism.
* Cytoskeleton: Internal framework of cells that provides support and helps with movement.
* εξωκυτταρική μήτρα: Network of molecules outside cells that provides structural support and communication.
4. Επικοινωνία και συντονισμός:
* Μεταγωγή σήματος: Cells communicate with each other through chemical messengers and receptors, coordinating activities.
* Ορμονική ρύθμιση: Cells respond to hormones released by specialized cells, regulating various processes.
* Νευρικό σύστημα: Specialized cells (neurons) transmit electrical impulses, enabling rapid communication and coordination.
5. Protection and Defense:
* ανοσοποιητικό σύστημα: Cells of the immune system (e.g., white blood cells) recognize and destroy pathogens, protecting the body from disease.
* Skin and mucous membranes: Cells form barriers that prevent entry of pathogens.
* επούλωση πληγών: Cells work together to repair damaged tissues.
6. Αναπαραγωγή:
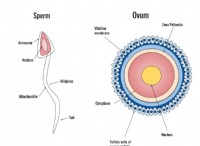
* Γαμετοί: Specialized cells (sperm and egg) carry genetic information for sexual reproduction.
* Εμβρυονική ανάπτυξη: Cells divide and differentiate to create a complete organism.
7. Αισθητηριακή αντίληψη:
* εξειδικευμένα κύτταρα: Cells in sensory organs (e.g., eyes, ears, skin) detect stimuli and convert them into signals that the nervous system can interpret.
These are just a few examples of the diverse and essential roles that cells play in the survival, growth, and function of all living organisms.