Does dissociation of salts keep salt molecules stable in water?
Εδώ είναι γιατί:
* Salt molecules are ionic compounds. They consist of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions) held together by electrostatic attraction.
* Το νερό είναι ένας πολικός διαλύτης. Its molecules have a positive end and a negative end.
* When salt dissolves in water, the water molecules surround the ions. The positive ends of water molecules attract the negative ions, and the negative ends of water molecules attract the positive ions.
* This attraction is strong enough to overcome the electrostatic forces holding the ions together in the salt molecule. This causes the salt molecule to break apart (dissociate) into its individual ions.
So, instead of keeping the salt molecules stable, the dissociation process separates the ions and makes them individually surrounded by water molecules, forming a solution.
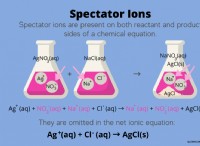
For example, when table salt (NaCl) dissolves in water, it dissociates into sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-):
NaCl(s) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
The (aq) indicates that the ions are now surrounded by water molecules and are in solution.